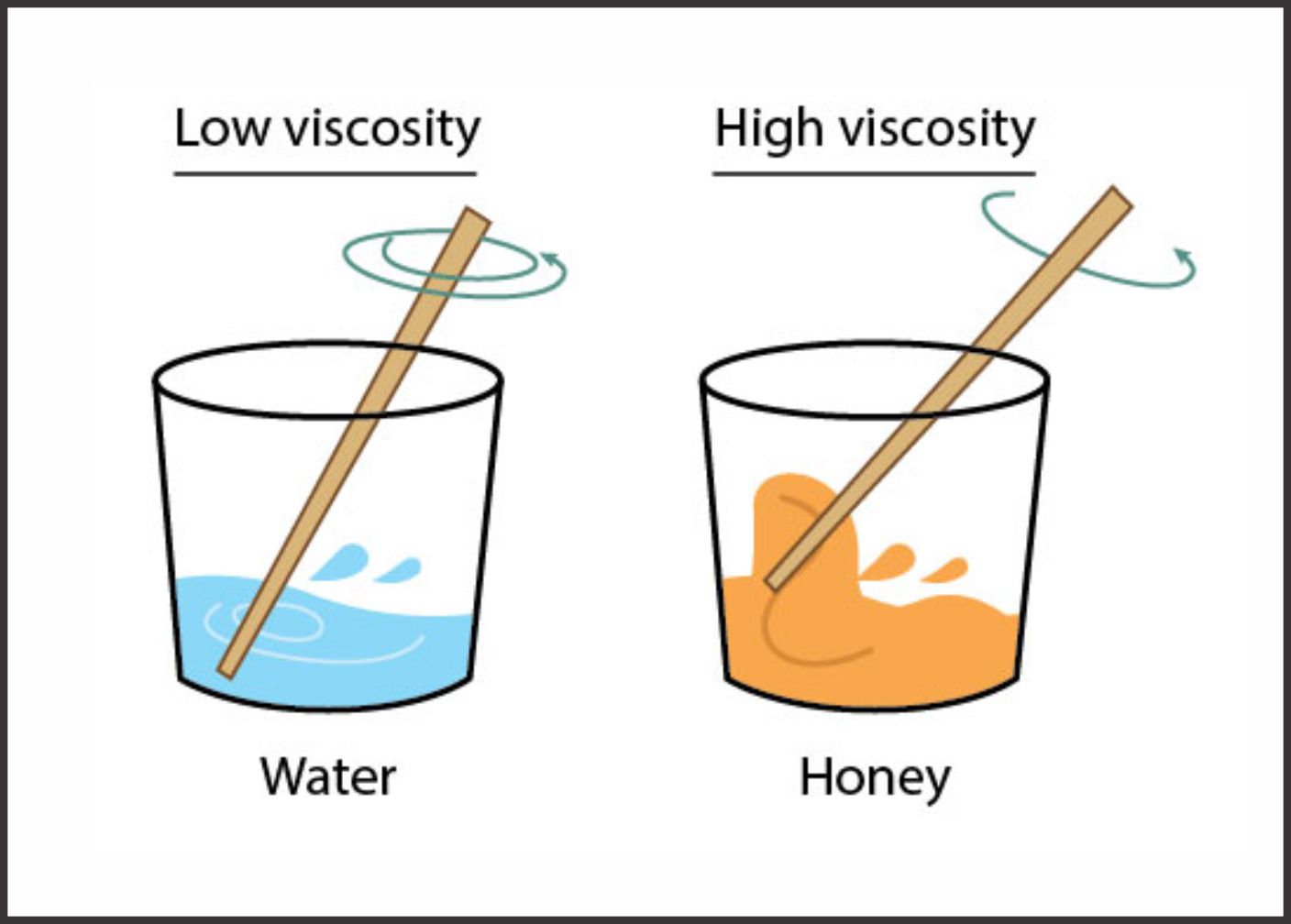
What is Viscosity?
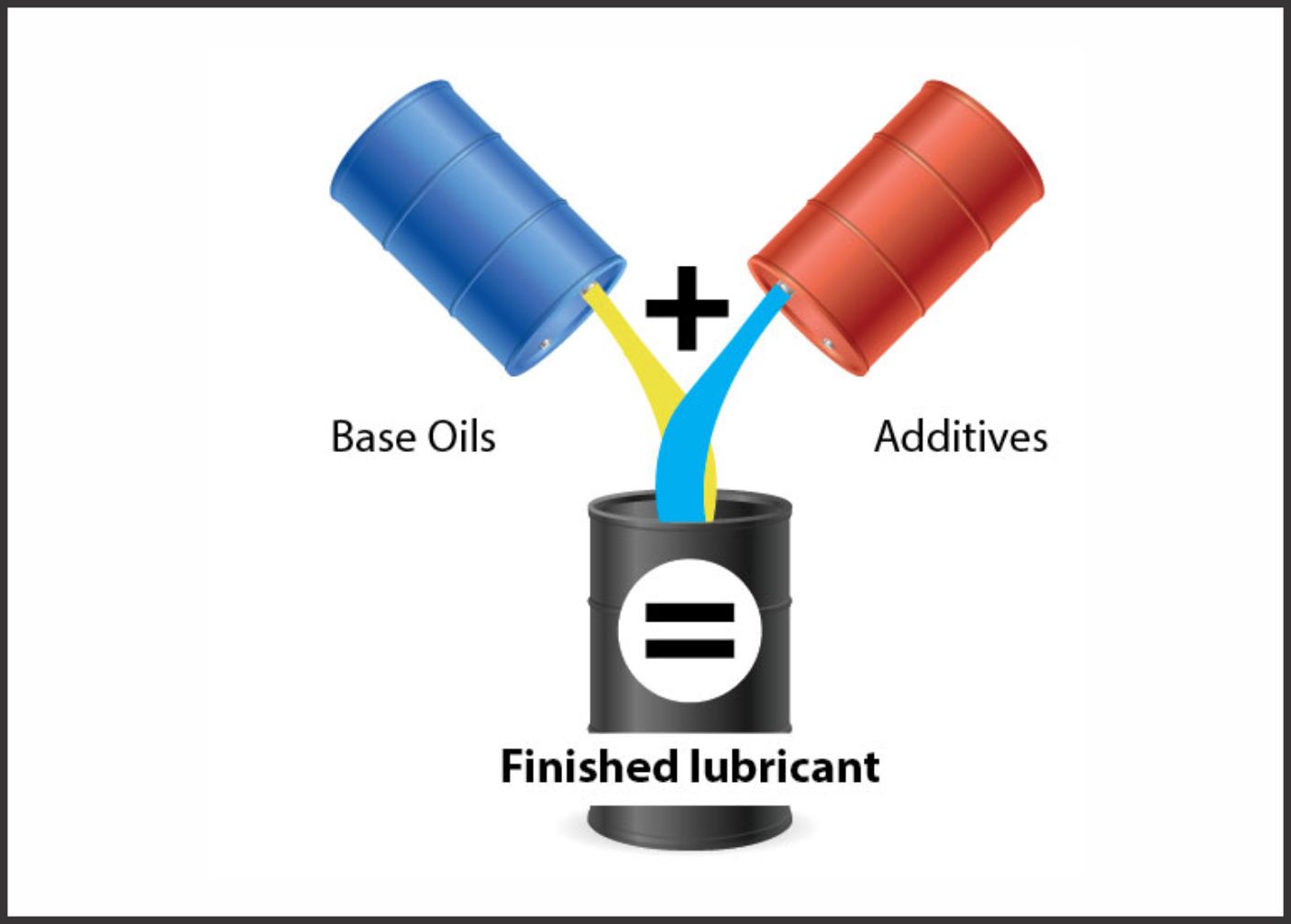
What is a Lubricant?
Lubricant generally is a liquid substance, which is used to reduce friction between surfaces. Based on the applications and the expected outcomes lubricant can be of different types like engine oil, transmission oil etc. A lubricant is made of two basic components: a. Base Oil b. Performance Additives Based on the advancement in technologies, high performance lubricant demands are increasing.
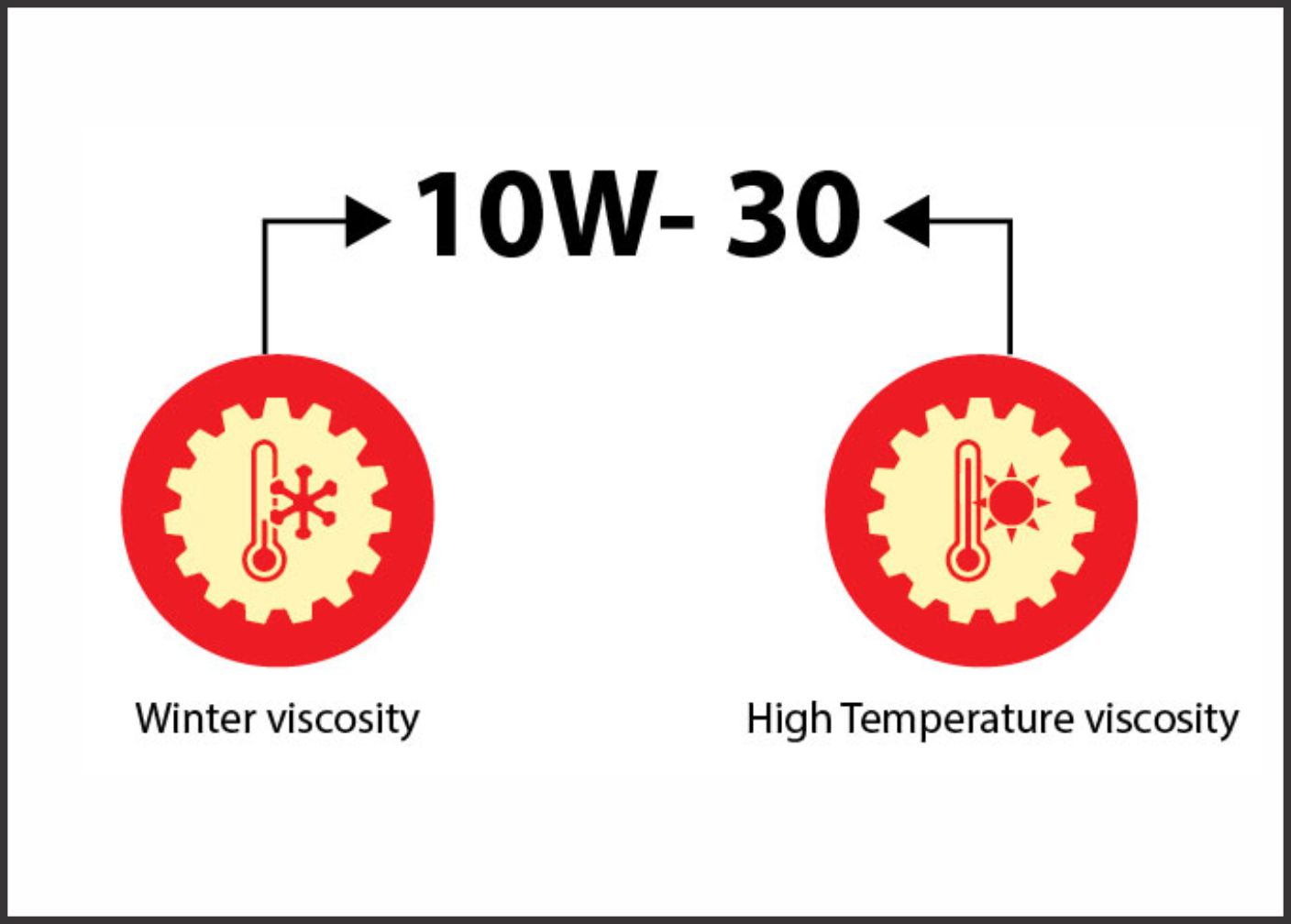
What is a Multi-grade Lubricant?
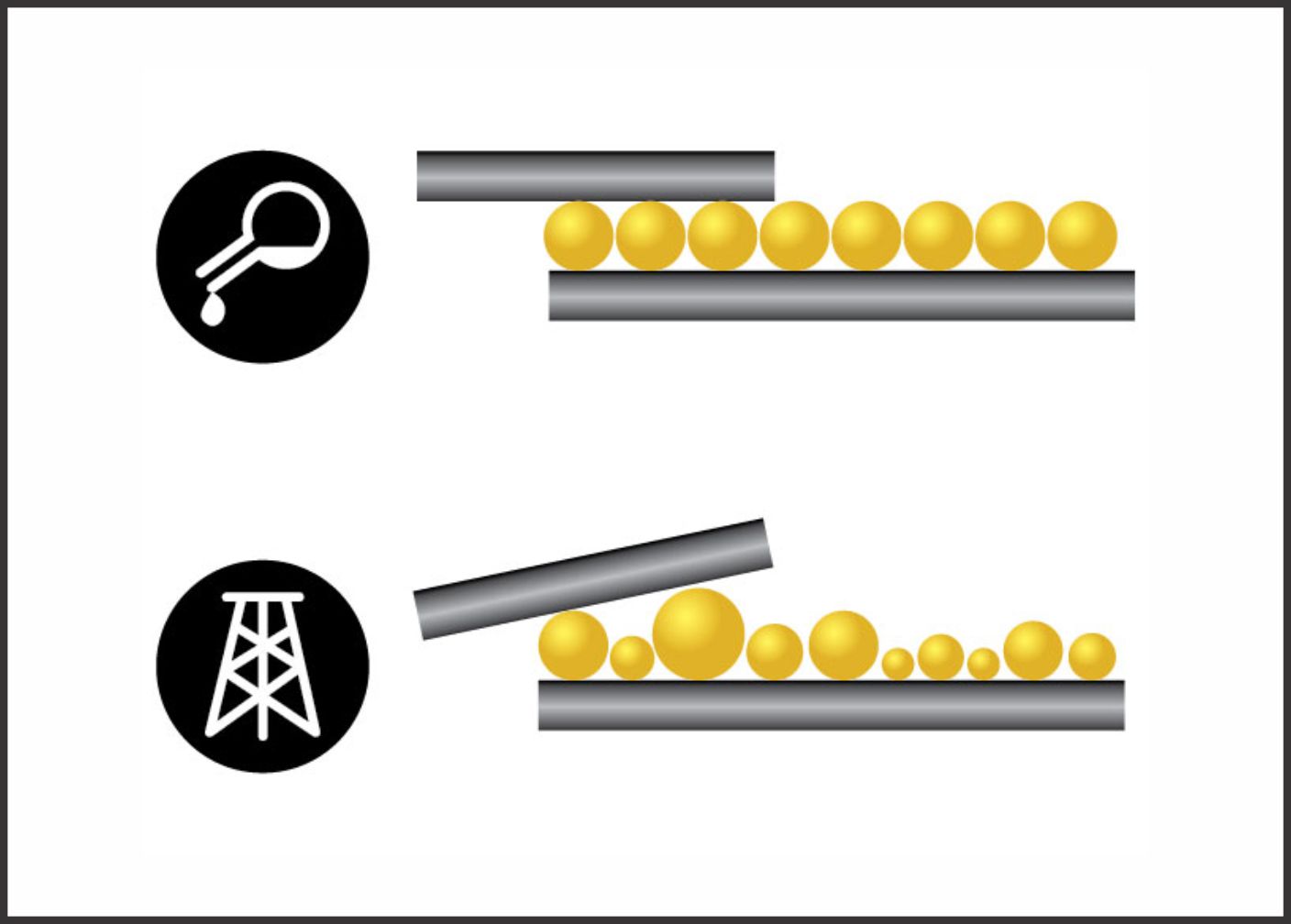
An oil's viscosity is defined by a numerical number, as decided by SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) for motor oils. This numerical code system defines grade of a motor oil based on its viscosity characteristics. For example: 30 or 40.
In general, there are two types of motor oils or lubricants available.
Mono-Grade Lubricants: Viscosity grade consist of only 1 number like 30 or 40 or 15W.
Multi-Grade Lubricants: Viscosity grade consists of two numbers 10W-30. 10W refers to the low-temperature viscosity ("Winter" in short "W"), 40 refers to the high-temperature viscosity.
Currently most of the automotive lubricants are multi-grade oils, capable to operate in wide temperate ranges.
What is a Synthetic Lubricant?
Synthetic oils are made with chemical compounds that are artificially manufactured. Generally, for automobile applications, lubricants are made with mineral base oils, which are derived from crude oil through distillation process. However, the quality of based oils can be further improved through advanced refining process. This produces high quality base oils which contain less impurity, less sulphur contents and have better viscosity index.
Lubricants can be segregated into 3 broad categories based on the kind of base oils and additives used:
Mineral: Manufactured with Group I & Group II base oils.
Semi Synthetic: Mineral oil with some proportion and benefits of Synthetic oil.
Fully
Synthetic: Developed with purest form of base oil like Group III and
above. Appropriate additives are also added in Semi Synthetic and
Fully synthetic oil to improve performance. 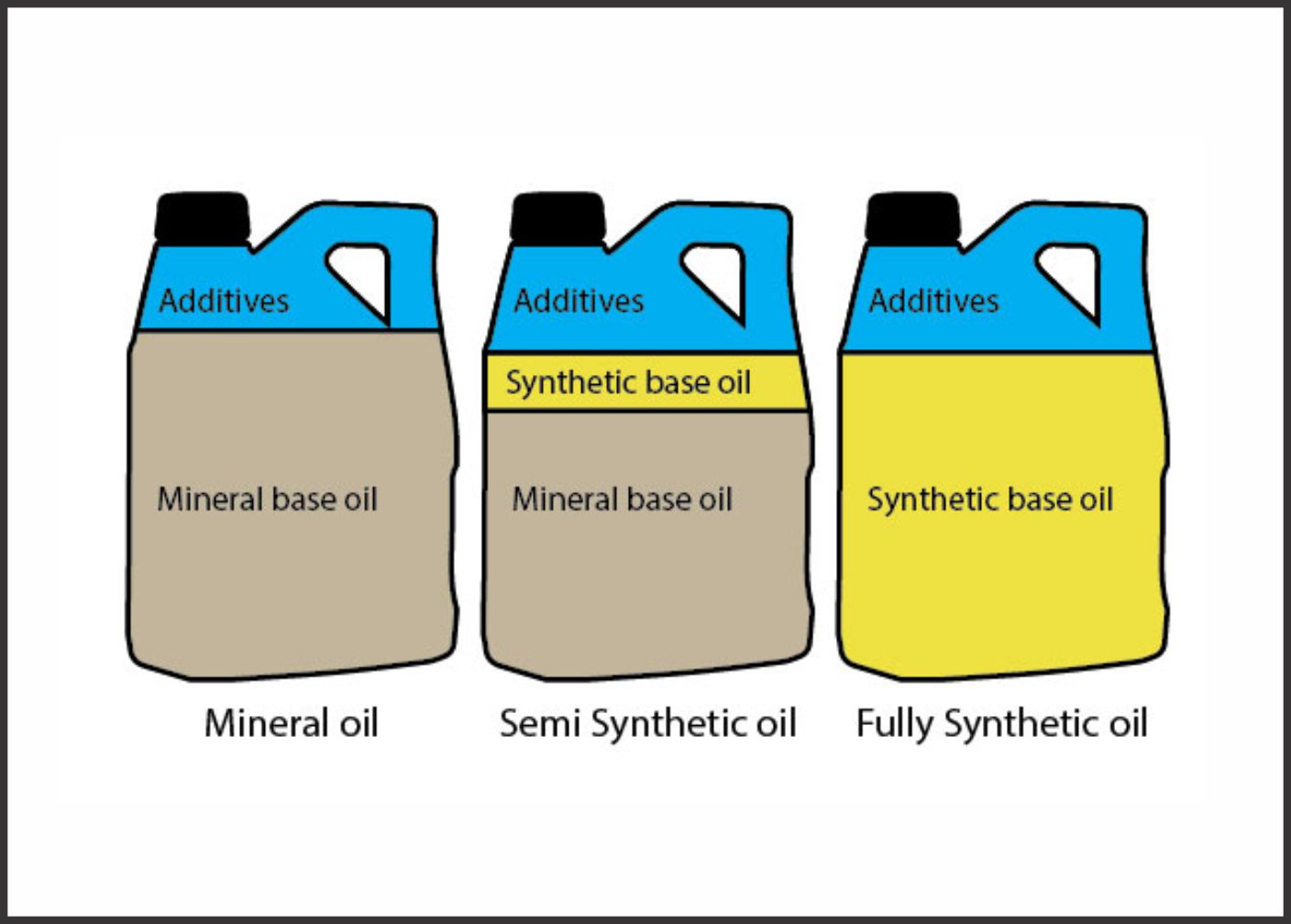
What are the benefits of Synthetic Oil over Mineral Oils?
Synthetic oils are manufactured with better quality base oils which have less impurities. The molecules of synthetic oils are more uniformed which helps the oil to perform more uniformly and efficiently.
Synthetic oils are generally designed to cope with extreme situation of modern engines and they come with loads of benefits:
Better protection from mechanical wear
Faster lubrication even in low temperature
Low oil consumption
Resistance to thermal break-down
Better engine cleanliness
Improved efficiency & fuel economy
Delayed oil degradation and many more
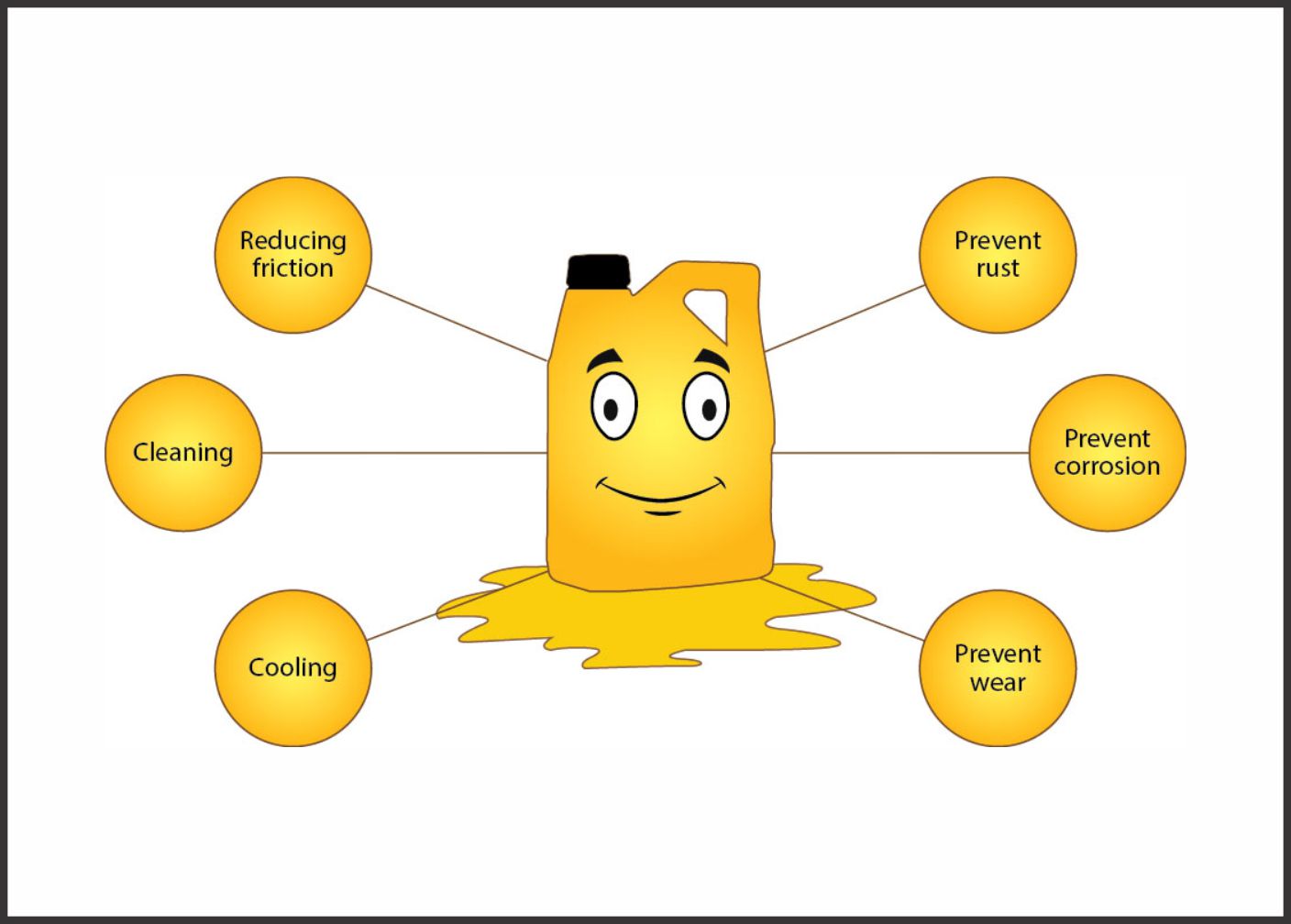
What are the functions of Engine Oil?
Engine oil's primary job is to provide lubricity to reduce friction between metal parts. However, this is not all, it also needs to do many other important jobs also like cleaning of engine parts, cooling, reduce oxidation and foaming, protection from mechanical wear and many more.
Why Engine Oil turns black?
One of the important functions of engine oil is "Cleaning". During operation, a lot of by-products and impurities are generated inside the engine like soot, dirt and other combustion contaminants. Engine oil's continuous & repeated exposure to heat cycles and oxidation also result into darkening of engine oil over a period of time. To keep engine protected, engine oils are developed with detergent additives, which continuously keeps these impurities in dispersed & suspended conditions so that during oil change all these dirt particles come out easily.